Connected Common Data Environment: Everything You Need to Know

The Engineering and Construction industry has long relied on Common Data Environments (CDEs) to manage project information and assets. Whether through a single platform or a group of integrated IT solutions, CDEs provide a centralised repository for collecting, managing, and disseminating project data. They are fundamental to the effective implementation of Building Information Management (BIM) processes and technologies.
However, many large businesses and joint ventures today often utilise multiple CDEs to handle various aspects of their projects. While this allows for specialisation, it also introduces challenges – platforms frequently operate in silos, making cross-CDE information sharing difficult, if not impossible. This fragmentation forces organisations to compromise, choosing solutions based on compatibility rather than suitability, leading to inefficiencies, errors, and wasted time.
With the goal of simplifying this challenge for those businesses that have multiple platforms, a Connected Common Data Environment fosters seamless data interoperability between platforms, ensuring that every software solution communicates efficiently and securely with the rest of the digital ecosystem.
What is a Connected Common Data Environment (or CDE 2.0)?
Connected Common Data Environment (or CDE 2.0) is a new approach to information management in AEC. It represents an interconnected ecosystem of CDEs, and software platforms designed to facilitate controlled data transfer across projects and organisations.
At its core, Connected Common Data Environment leverages an Open CDE philosophy that is data agnostic to maximise the range of authoring tools that can operate within the environment. Furthermore, technologies such as DataFlows enable seamless communication between multiple CDEs for businesses that use them, eliminating data silos. This allows businesses to select the best-in-class solutions without the concern of incompatibility.
Additionally, it aligns with industry security standards and ISO requirements, ensuring that data transfers are controlled, structured, and compliant. The approach not only streamlines collaboration but also enhances flexibility in information management.
The Goals of Connected Common Data Environments
Connected Common Data Environment is designed to break down the barriers that traditional CDEs impose faced by some businesses in the industry. The key objectives include:
- Eliminating Data Silos: Ensuring seamless, secure, and structured data exchange between platforms.
- Enhancing Flexibility: Enabling businesses to choose software solutions based on functionality rather than compatibility constraints.
- Ensuring Compliance: Supporting ISO 19650 workflows to ensure that data transfers follow formal approval processes before being published in another CDE.
- Saving Time: Allowing automatic and trackable data transfer and eliminating the time it took resources to manually send and receive it.
- Future-Proofing: Avoiding vendor lock-in and enabling adaptability to new software solutions over long project timelines.
The transition to CDE 2.0 empowers businesses to move beyond monolithic solutions, giving them the freedom to work with multiple best-in-breed tools without compromising data accessibility or security.
Open CDEs vs. Closed CDEs: Choosing the Right Approach
For businesses looking to adopt a CDE, understanding the distinction between open and closed CDEs is critical.
Closed CDEs: The Restrictive Model
Many CDEs operate as closed environments, meaning they only integrate within their own suite of tools. While this can be suitable for some projects, it can also restrict connectivity with other solutions, effectively locking businesses into a specific vendor’s ecosystem. While this may provide a seamless experience within that suite, it severely limits flexibility, making it difficult to incorporate new technologies over time.
For projects that span years or even decades, this lack of adaptability becomes a significant drawback. As new software solutions emerge, businesses relying on closed CDEs may find themselves constrained by their existing infrastructure, unable to leverage innovative tools that could enhance efficiency and effectiveness.
Open CDEs: The Key to CDE 2.0
In contrast, open CDEs embrace interoperability, supporting data transfer and connectivity with a wide range of software solutions. This vendor-agnostic approach provides businesses with the ability to choose from the broadest selection of authoring tools, ensuring that future project requirements can be met with the most suitable technologies available.
An open CDE strategy not only maximises flexibility but also future proofs an organisation’s technology stack, allowing it to integrate with emerging tools effortlessly. By participating in the CDE 2.0 ecosystem, open CDEs ensure that businesses are not constrained by a single vendor but can instead harness the full potential of the digital landscape.
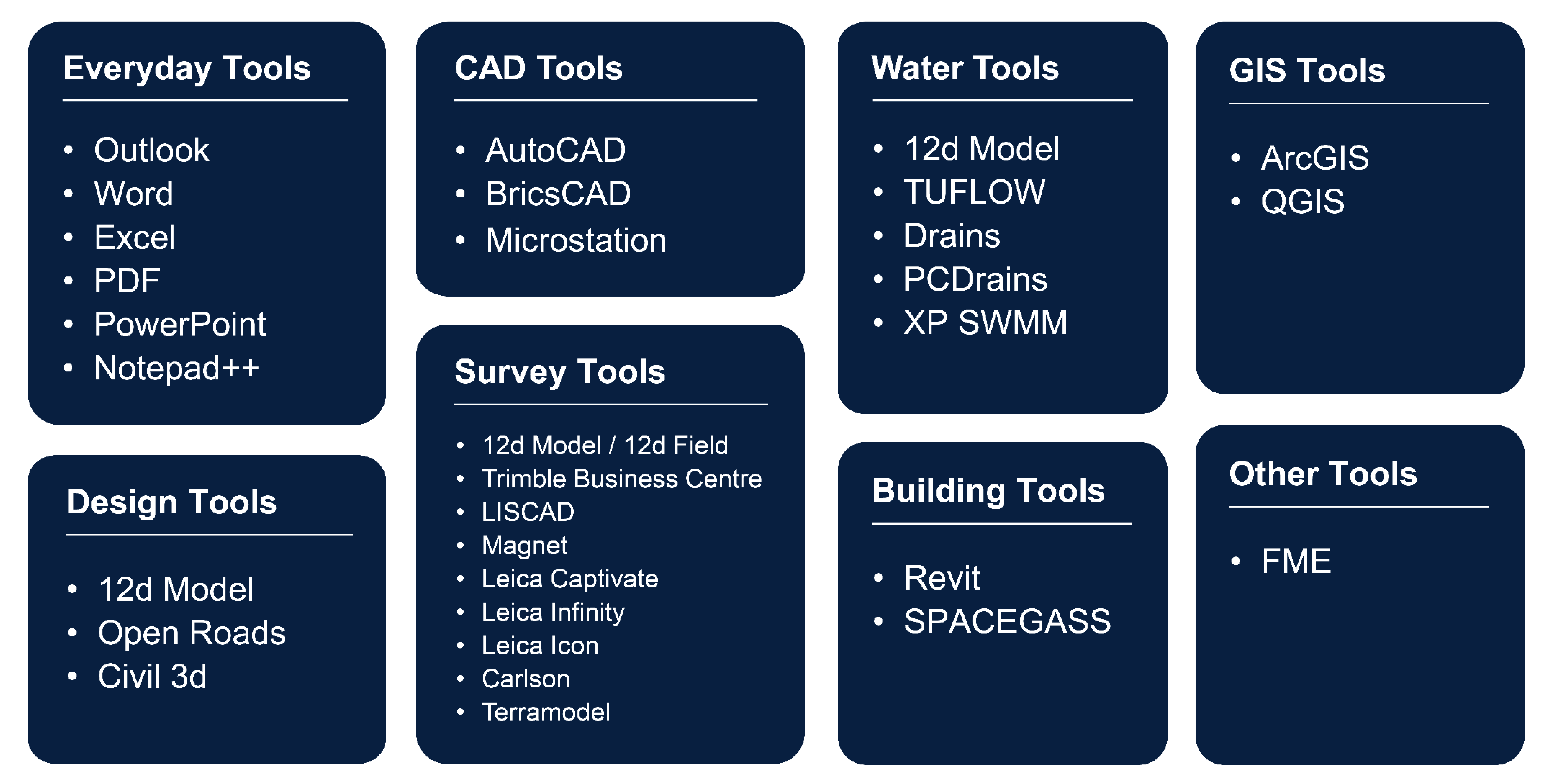
Enabling Connected CDEs with a Data-Agnostic Approach
For businesses shifting to a Connected CDE setup, platforms like 12d Synergy are leading the way by providing a vendor-agnostic, open data environment.
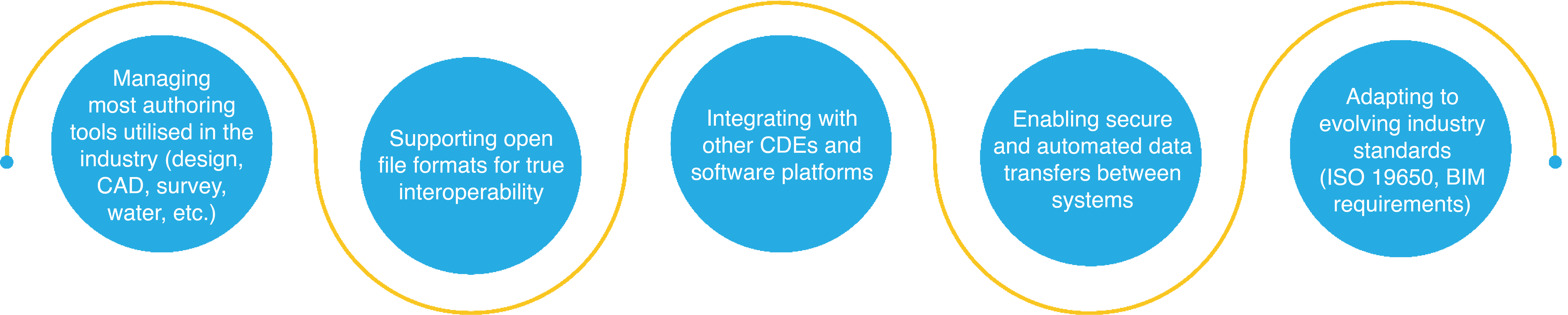
12d Synergy’s approach to a Connected CDE is driven by:
- Managing most authoring tools utilised in the industry (design, CAD, survey, water, etc.).
- Supporting open file formats for true interoperability.
- Integrating with other CDEs and software platforms.
- Enabling secure and automated data transfers between systems.
- Adapting to evolving industry standards (ISO 19650, BIM requirements).
Unlike closed solutions that restrict software choices, 12d Synergy empowers businesses to select the best-in-class authoring tools without worrying about compatibility issues.
By embracing data flexibility and open integration, 12d Synergy is helping AEC businesses unlock the full potential of CDE 2.0—where information is managed across authoring tools and flows freely, efficiently, and securely across software platforms.
The Future of Data Management in AEC
As projects grow in complexity and technology choices constantly evolve, the need for Open CDEs becomes clear.
By embracing data agnostic solutions and prioritising interoperability, businesses can futureproof their operations, benefit from greater flexibility, improved collaboration, and enhanced efficiency – all while maintaining strict security and compliance standards.
By choosing Open CDEs, organisations can ensure they remain agile and competitive in an ever-evolving industry
Ready to implement a Connected Common Data Environment?
